|
Listen to this article
|

Chinese and U.S. companies led March 2024 robotics investments. Credit: Eacon Mining, Dan Kara
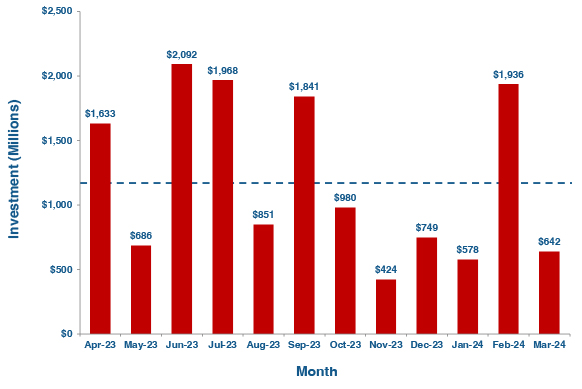
Thirty-seven robotics firms received funding in March 2024, pulling in a total monthly investment of $642 million. March’s investment figure was significantly less than February’s mark of approximately $2 billion, but it was in keeping with other monthly investments in 2023 and early 2024 (see Figure 1, below).
California companies secure investment
As described in Table 1 below, the two largest robotics investments in March were secured by software suppliers. Applied Intuition, a provider of software infrastructure to deploy autonomous vehicles at scale, received a $250 million Series E round, while Physical Intelligence, a developer of foundation models and other software for robots and actuated devices, attracted $70 million in a seed round. Both firms are located in California.
Other California firms receiving substantial rounds included Bear Robotics, a manufacturer of self-driving indoor robots that raised a $60 million Series C round, and unmanned aerial system (UAS) developer Firestorm, whose seed funding was $20 million. For a PDF version of Table 1, click here.
March 2024 robotics investments
| Company | Amount ($) | Round | Country | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agilis Robotics | 10,000,000 | Series A | China | Surgical/interventional systems |
| Aloft | Estimate | Other | U.S. | Drones, data acquisition / processing / management |
| Applied Intuition | 250,000,000 | Series E | U.S. | Software |
| Automated Architecture | 3,280,000 | Estimate | U.K. | Micro-factories |
| Bear RoboBear Roboticstics | 60,000,000 | Series C | U.S. | Indoor mobile platforms |
| BIOBOT Surgical | 18,000,000 | Series B | Singapore | Surgical systems |
| Buzz Solutions | 5,000,000 | Other | U.S. | Drone inspection |
| Cambrian Robotics | 3,500,000 | Seed | U.K. | Machine vision |
| Coctrl | 13,891,783 | Series B | China | Software |
| DRONAMICS | 10,861,702 | Grant | U.K. | Drones |
| Eacon Mining | 41,804,272 | Series C | China | Autonomous transportation, sensors |
| ECEON Robotics | Estimate | Pre-seed | Germany | Autonomous forklifts |
| ESTAT Automation | Estimate | Grant | U.S. | Actuators / motors / servos |
| Fieldwork Robotics | 758,181 | Grant | U.K. | Outdoor mobile manipulation platforms, sensors |
| Firestorm Labs | 20,519,500 | Seed | U.S. | Drones |
| Freespace Robotics | Estimate | Other | U.S. | Automated storage and retrieval systems |
| Gather AI | 17,000,000 | Series A | U.S. | Drones, software |
| Glacier | 7,700,000 | Other | U.S. | Articulated robots, sensors |
| IVY TECH Ltd. | 421,435 | Grant | U.K. | Outdoor mobile platforms |
| KAIKAKU | Estimate | Pre-seed | U.K. | Collaborative robots |
| KEF Robotics | Estimate | Grant | U.S. | Drone software |
| Langyu Robot | Estimate | Other | China | Automated guided vehicles, software |
| Linkwiz | 2,679,725 | Other | Japan | Software |
| Motional | Estimate | Seed | U.S. | Autonomous transportation systems |
| Orchard Robotics | 3,800,000 | Pre-seed | U.S. | Crop management |
| Pattern Labs | 8,499,994 | Other | U.S. | Indoor and outdoor mobile platforms |
| Physical Intelligence | 70,000,000 | Seed | U.S. | Software |
| Piximo | Estimate | Grant | U.S. | Indoor mobile platforms |
| Preneu | 11,314,492 | Series B | Korea | Drones |
| QibiTech | 5,333,884 | Other | Japan | Software, operator services, uncrewed ground vehicles |
| Rapyuta Robotics | Estimate | Other | Japan | Indoor mobile platforms, autonomous forklifts |
| RIOS Intelligent Machines | 13,000,000 | Series B | U.S. | Machine vision |
| RITS | 13,901,825 | Series A | China | Sensors, software |
| Robovision | 42,000,000 | Other | Belgium | Computer vision, AI |
| Ruoyu Technology | 6,945,312 | Seed | China | Software |
| Sanctuary Cognitive Systems | Estimate | Other | Canada | Humanoids / bipeds, software |
| SeaTrac Systems | 899,955 | Other | U.S. | Uncrewed surface vessels |
| TechMagic | 16,726,008 | Series C | Japan | Articulated robots, sensors |
| Thor Power | Estimate | Seed | China | Articulated robots |
| Viam | 45,000,000 | Series B | Germany | Smart machines |
| WIRobotics | 9,659,374 | Series A | S. Korea | Exoskeletons, consumer, home healthcare |
| X Square | Estimate | Seed | U.S. | Software |
| Yindatong | Estimate | Seed | China | Surgical / interventional systems |
| Zhicheng Power | Estimate | Series A | China | Consumer / household |
| Zhongke Huiling | Estimate | Seed | China | Humanoids / bipeds, microcontrollers / microprocessors / SoC |
Drones get fuel for takeoff in March 2024
Providers of drones, drone technologies, and drone services also attracted substantial individual investments in March 2024. Examples included Firestorm and Gather AI, a developer of inventory monitoring drones whose Series A was $17 million.
In addition, drone services provider Preneu obtained $11 million in Series B funding, and DRONAMICS, a developer of drone technology for cargo transportation and logistics operations, got a grant worth $10.8 million.
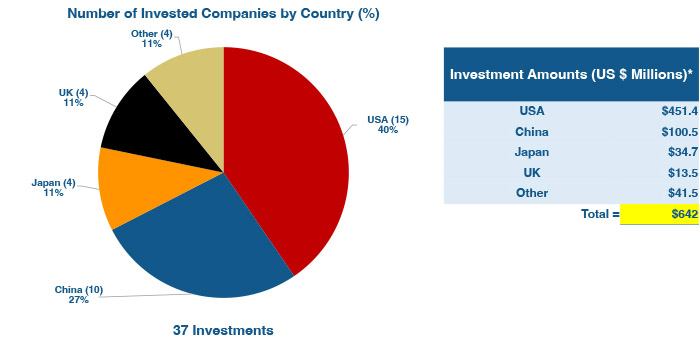
Companies in U.S. and China received the majority of the March 2024 funding, at $451 million and $100 million, respectively (see Figure 2, below).
Companies based in Japan and the U.K. were also well represented among the March 2024 investment totals. Four companies in Japan secured a total of $34.7 million, while an equal number of firms in the U.K. attracted $13.5 million in funding.
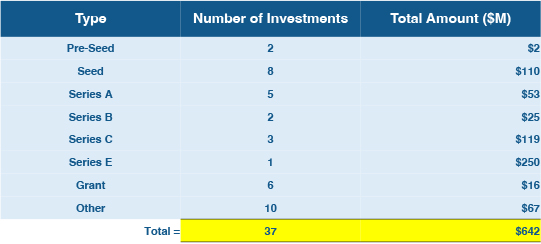
Nearly 40% of March’s robotics investments came from a single Series E round — that of Applied Intuition. The remaining funding classes were all represented in March 2024 (Figure 3, below).
Editor’s notes
What defines robotics investments? The answer to this simple question is central in any attempt to quantify them with some degree of rigor. To make investment analyses consistent, repeatable, and valuable, it is critical to wring out as much subjectivity as possible during the evaluation process. This begins with a definition of terms and a description of assumptions.
Investors and investing
Investment should come from venture capital firms, corporate investment groups, angel investors, and other sources. Friends-and-family investments, government/non-governmental agency grants, and crowd-sourced funding are excluded.
Robotics and intelligent systems companies
Robotics companies must generate or expect to generate revenue from the production of robotics products (that sense, analyze, and act in the physical world), hardware or software subsystems and enabling technologies for robots, or services supporting robotics devices. For this analysis, autonomous vehicles (including technologies that support autonomous driving) and drones are considered robots, while 3D printers, CNC systems, and various types of “hard” automation are not.
Companies that are “robotic” in name only, or use the term “robot” to describe products and services that do not enable or support devices acting in the physical world, are excluded. For example, this includes “software robots” and robotic process automation. Many firms have multiple locations in different countries. Company locations given in the analysis are based on the publicly listed headquarters in legal documents, press releases, etc.
Verification
Funding information is collected from several public and private sources. These include press releases from corporations and investment groups, corporate briefings, market research firms, and association and industry publications. In addition, information comes from sessions at conferences and seminars, as well as during private interviews with industry representatives, investors, and others. Unverifiable investments are excluded and estimates are made where investment amounts are not provided or are unclear.






Tell Us What You Think!