|
Listen to this article
|
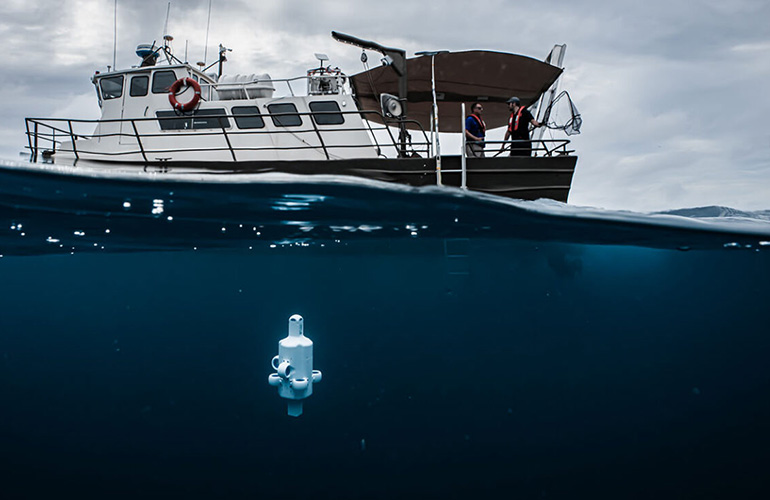

Advanced Navigation’s Hydrus micro autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) deployed. | Source: Advanced Navigation
Advanced Navigation is bringing humans closer to the ocean with Hydrus, a relatively small underwater drone. The company recently sent Hydrus to the depths of the Rottnest ship graveyard, located in the Indian Ocean and just off the coast of Western Australia.
The Sydney, Australia-based developer of AI robotics and navigation technology said that upon seeing the gathered data, the team discovered a 210-ft. (64-m) shipwreck scattered across the sea floor. This means the wreck was more than twice the size of a blue whale.
“We’ve found through all of our testing that Hydrus is very reliable, and it will complete its mission and come to the surface or come to its designated return point,” Alec McGregor, Advanced Navigation’s photogrammetry specialist, told The Robot Report. “And then you can just scoop it up with a net from the side of the boat.”
Robot can brave the ocean’s unexplored depths
Humans have only explored and charted 24% of the ocean, according to Advanced Navigation. The unexplored parts are home to more than 3 million undiscovered shipwrecks, and 1,819 recorded wrecks are lying off Western Australia’s shore alone.
These shipwrecks can hold keys to our understanding of past culture, history, and science, said the company.
The Rottnest graveyard is a particularly dense area for these abandoned ships. Beginning in the 1900s, the area became a burial ground for ships, naval vessels, aircraft, and secretive submarines. A majority of these wrecks haven’t been discovered because the depth ranges from 164 to 656 ft. (50 to 200 m).
Traditionally, there are two ways of gathering information from the deep sea, explained McGregor. The first is divers, who have to be specially trained to reach the depths Advanced Navigation is interested in studying.
“Some of the wrecks that we’ve been looking at are in very deep water, so 60 m [196.8 ft.] for this particular wreck, which is outside of the recreational diving limit,” McGregor said. “So, you actually have to go into tech diving.”
“And when you go deeper with all of this extra equipment, it tends to just increase the risks associated with going to depth,” he said. “So, you need to have special training, you need to have support vessels, and you also have to be down in the water for a long period of time.”
The second option is to use remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) or autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs). While this method doesn’t involve putting people at risk, it can still be expensive.
“Some of the drawbacks with using traditional methods include having to have big support vessels,” McGregor said. “And getting the actual ROVs in and out of the water sometimes requires a crane, whereas with the Hydrus, you can just chuck it off the side of the boat.”
“So, with Hydrus, you’re able to reduce the costs of operation,” he added. “You’re also able to get underwater data super easily and super quickly by just chucking a Hydrus off the boat. It can be operated with one person.”
Advanced Navigation uses ‘wet electronics’
One of the biggest challenges with underwater robotics, McGregor said, is keeping important electronics dry. Conventional ROVs do this with pressure chambers.
“Traditional ROVs have big chambers which basically keep all the electronics dry,” he noted. “But from a mechanical point of view, if you want to go deeper, you need to have thicker walls so that they can resist the pressure at depth.”
“If you need thicker walls, that increases the weight of the robot,” said McGregor. “And if you increase the weight, but you still want the robot to be buoyant, you have to increase the size. It’s just this kind of spiral of increasing the size to increase the buoyancy.”
“What we’ve managed to do with Hydrus is we have designed pressure-tolerant electronics, and we use a method of actually having what we call ‘wet electronics,'” McGregor said. “This involves basically potting the electronics in a plastic material. And we don’t use it to keep the structural integrity of the robot. So we don’t need a pressure vessel because we’ve managed to protect our electronics that way.”
Once it’s underwater, Hydrus operates fully autonomously. Unlike traditional ROVs, the system doesn’t require a tether to navigate underwater, and the Advanced Navigation team has limited real-time communication capabilities.
“We do have very limited communication with Hydrus through acoustic communications,” McGregor said. “The issue with acoustic communications is that there’s not a lot of data that can be transferred. We can get data such as the position of Hydrus, and we can also send simple commands such as ‘abort mission’ or ‘hold position’ or ‘pause mission,’ but we can’t physically control it.”
Hydrus provides high-resolution data
While Hydrus has impressive autonomous capabilities, it doesn’t find wrecks all on its own. In this case, McGregor said, Advanced Navigation worked closely with the Western Australian (WA) Museum to find the wreck.
The museum gave the company a rough idea of where a shipwreck could be. Then the team sent Hydrus on a reconnaissance mission to determine the wreck’s exact location.
“When we got Hydrus back on board, we were able to offload all the data and reconstruct the mission based on the images and from that, we were then able to see where the shipwreck was,” McGregor said. “One of the good things about Hydrus is that we can actually get geo-referenced data onto the water with auxiliary systems that we have on the boat.”
Hydrus gathered 4K geo-referenced imagery and video footage. Curtin University HIVE, which specializes in shipwreck photogrammetry, used this data to rebuild a high-resolution 3D digital twin of the wreck. Ross Anderson, a curator at the WA Museum, closely examined the digital twin.
Anderson found that the wreck was an over 100-year-old coal hulk from Fremantle Port’s bygone days. Historically, these old iron ships were used to service steamships in Western Australia.
In the future, the team is interested in exploring other shipwrecks, like the SS Koombana, an ultra-luxury passenger ship. The ship ferried more than 150 passengers before it vanished into a cyclone in 1912.
However, Advanced Navigation isn’t just interested in gaining information from shipwrecks.
“Another thing we’re doing with a lot of this data is actually coral reef monitoring. So we’re making 3D reconstructions of coral reefs, and we’re working with quite a few customers to do this,” McGregor said.
Hydrus reduced the surveying costs for this particular mission by up to 75%, according to the company. This enabled the team to conduct more frequent and extensive surveying of the wreck in a shorter period of time.






Tell Us What You Think!